Aspiration Pneumonia in Elderly Nursing Home Patients
Aspiration Pneumonia Can Be Prevented in Nursing Home Residents
Pneumonia is a serious infection of one or both lungs. The most common types of pneumonia are viral pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia caused by the flu virus and Streptococcus bacteria, respectively.
However, there are a multitude of other types of pneumonia.
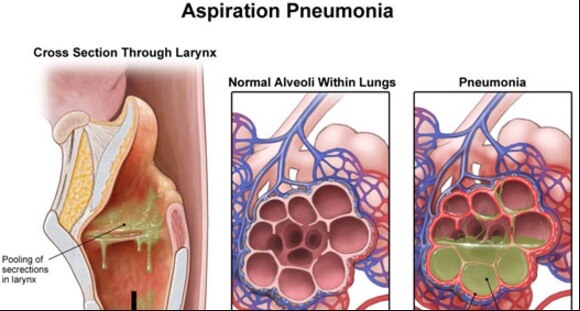
A special type of pneumonia called aspiration pneumonia is a lung infection that occurs after food, blood, stomach acid, or vomit is aspirated, or inhaled, into the lungs.
Though it is not the most common type of pneumonia, aspiration pneumonia is a life-threatening and largely preventable disease.
In a 2013 study, it was calculated that 21% of cases involving aspiration pneumonia culminated in death within 30 days. Most cases of aspiration pneumonia in nursing homes and hospitals could have been prevented through appropriate supervision from the staff. If an aspiration pneumonia event results in the wrongful death of the patient, a nursing home abuse lawsuit should be considered.
What Causes Aspiration Pneumonia in Nursing Home Patients?
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of pneumonia that occurs when food, saliva, liquids, or vomit are breathed into the lungs instead of being swallowed into the stomach. Nursing home residents are at a higher risk of developing aspiration pneumonia, so it is the legal duty of the nursing home to attempt to prevent aspiration pneumonia.
Firstly, older adults may have weakened immune systems and respiratory muscles, making them more vulnerable to infections and respiratory illnesses. Additionally, some nursing home residents may have underlying medical conditions such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or dementia, which can affect their ability to swallow and increase the risk of aspiration.
Secondly, nursing home residents may require assistance with eating and drinking, and may have difficulties communicating their needs to staff. This can result in improper feeding by nursing home staff, or the nursing home giving the resident inappropriate diets, which may lead to aspiration.
Thirdly, nursing home residents may be at increased risk of aspiration due to their position during meals. The standard of care dictates that an aspiration-risk resident eats propped up, not while lying down. Individuals who are bedridden or who have difficulty sitting upright may be more likely to aspirate food or liquids into their lungs. This is particularly true in patients with a feeding tube.
Fourthly, nursing home staff must observe and assist at-risk residents during meals and snacks. A CNA should physically sit with the resident to make sure they are only eating small, or soft mechanical bites, and to make sure the resident is not choking.
Finally, some medications that are commonly prescribed to nursing home residents, such as sedatives, may increase the risk of aspiration by impairing their ability to protect their airway.
To prevent aspiration pneumonia, nursing home staff should ensure that residents are receiving appropriate diets and assistance with feeding, maintain a clean and safe environment, and monitor residents for signs of aspiration, such as coughing or choking during meals.
Additionally, nursing home residents who are at high risk of aspiration may benefit from interventions such as speech therapy or modified diets to reduce the risk of aspiration.
Experience Matters. Our Attorneys Have It.
Symptoms of Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a lung infection due to a foreign material (food, blood, vomit) that is aspirated (inhaled) into the lungs. In aspiration pneumonia, the bacteria and microorganisms within the aspirated material will infect the lungs.
Material inhaled into the lungs can also damage lung tissue and cause inflammation. Symptoms of aspiration pneumonia include:
- coughing,
- sputum (mucus coughed up from the lungs),
- shortness of breath,
- chest pain,
- difficulty swallowing,
- fever,
- malaise, and
- confusion.
Aspiration pneumonia is confirmed through blood and sputum analyses, swallowing tests, X-ray and CT imaging, and/or a bronchoscopy.
Patients with aspiration pneumonia typically have bouts of coughing or trouble breathing. If the nurses ignore the patient’s difficulty with breathing, they may be ignoring this life-threatening infection.
Causes of Aspiration Pneumonia in a Nursing Home
Aspiration pneumonia can be caused by:
- inappropriate food given to a swallowing-impaired resident
- food not being cut up into small pieces
- insufficient supervision while an impaired resident eats their food
- uncontrolled coughing which leads to food or mucus entering the lungs
- tube feeding a resident while lying flat on their back (not elevating the bed during feedings)
Treatment of Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia can be treated if discovered early enough.
Treatment for aspiration pneumonia involves determining the strain of bacteria causing the infection, administering the appropriate antibiotics, supplying oxygen support, and providing mechanical ventilation if necessary. In severe cases, surgery is performed in order to remove fluid from the lungs or to install a chest tube. If these treatments are not applied soon enough, aspiration pneumonia can be fatal.
Aspiration Pneumonia in Nursing Home Patients
The elderly have a higher probability of acquiring aspiration pneumonia due to underlying conditions commonly found in the geriatric population. These underlying conditions include the following:
- Impaired gag reflex due to stroke or neurological disease (i.e. Parkinson’s, Huntington’s or Alzheimer’s disease)
- Difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, due to cancerous strictures on the esophagus, mechanical ventilation, or neurological disease
- Impaired ability to cough or expel aspirated material due to age or sedation
- Presence of a feeding tube
- Compromised immune response due to age, disease, or immunosuppressant medications
Preventative steps should be taken in situations where a patient is predisposed to aspiration. The patient’s bed should be kept at a 30˚- 45˚ incline.
At-risk patients’ diets should consist of soft foods that are eaten in small increments with frequent swallowing, the chin tucked and the head turned. Frequent oral care (teeth brushing or mouth swabbing) should be given so as to reduce the presence of bacteria and food in the patient’s saliva.
Medication is recommended in some situations in order to reduce stomach acidity, since there is an increased risk of gastric acid entering the lungs.
Wrongful Death Lawsuits Regarding Aspiration Pneumonia
Pneumonia and respiratory tract infections are one of the leading cause for death in nursing home and extended care facilities. Recovery from pneumonia in elderly patients is a long and arduous process. Many incidents of pneumonia are not preventable; however, aspiration pneumonia is an easily recognizable and treatable medical event.
As a consequence, it is vital that caretakers remain alert to an elderly person’s predisposition to aspiration and any symptoms of pneumonia that appear. Unfortunately, many incidents of aspiration pneumonia involve malpractice and negligence (i.e. failure to monitor a patient after eating, improper placement of feeding tubes, improper monitoring during anesthesia).
Has Your Loved One Suffered From Aspiration Pneumonia Under the Care of a Facility? Receive A Free Consultation
Our narrowly focused nursing home neglect attorneys have handled hundreds of aspiration pneumonia wrongful death cases. If you lost a family member due to aspiration pneumonia while in the care of a nursing home, speak with our law firm today to learn more about your legal rights. The call is free. Learn more about how Senior Justice Law Firm can help by calling us at (888) 375-9998.

